- The CyberLens Newsletter
- Posts
- Identity-Native Security Architecture The New Foundation of Digital Trust
Identity-Native Security Architecture The New Foundation of Digital Trust
Where digital trust becomes engineered instead of assumed

Attention spans are shrinking. Get proven tips on how to adapt:
Mobile attention is collapsing.
In 2018, mobile ads held attention for 3.4 seconds on average.
Today, it’s just 2.2 seconds.
That’s a 35% drop in only 7 years. And a massive challenge for marketers.
The State of Advertising 2025 shows what’s happening and how to adapt.
Get science-backed insights from a year of neuroscience research and top industry trends from 300+ marketing leaders. For free.

🖥️ Interesting Tech Fact:
One of the first computerized identity access systems was quietly deployed at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory to manage time-sharing access across shared mainframes — but what made it groundbreaking was that it logged every user command for anomaly review decades before modern SIEMs existed. Engineers manually reviewed printouts to detect misuse patterns, unintentionally pioneering behavioral monitoring long before the term existed. That primitive experiment planted early seeds of identity telemetry thinking long before cloud computing ever emerged 📜🔍.
Introduction
In every generation of computing, there comes a moment when the old mental models collapse under the weight of new realities. Firewalls once defined safety. Network zones once implied control. Perimeters once separated trusted systems from untrusted ones. That era is gone. Cloud-native infrastructure, AI-driven automation, remote workforces, machine identities, ephemeral workloads, and decentralized services have dissolved the boundaries that security teams once relied upon. What remains constant is identity — the one attribute every system, user, workload, API, and device must carry to function in a connected ecosystem.
Identity-Native Security Architecture represents a structural shift in how trust is engineered, enforced, and verified across modern environments. Instead of wrapping identity around infrastructure as an add-on, identity becomes the foundation upon which access, policy, telemetry, automation, and governance are built. Every transaction becomes an identity event. Every decision becomes a verification exercise. Every workload becomes accountable. For organizations seeking resilience in a world where breaches increasingly originate from valid credentials rather than malware exploits, identity-native design is no longer optional — it is becoming operational survival.

Why Identity Now Defines the Primary Attack Surface
The most sophisticated cyber incidents of the past decade have shared a common pattern: attackers rarely break in; they log in. Phished credentials, stolen tokens, exposed service accounts, compromised OAuth flows, API abuse, and session hijacking dominate modern breach reports. As enterprises embrace automation, DevOps pipelines, SaaS platforms, container orchestration, AI agents, and multi-cloud architectures, the number of identities multiplies rapidly. Each micro-service carries credentials. Each pipeline executes under permissions. Each bot authenticates. Each vendor integration introduces access paths. The attack surface is no longer the network — it is the identity fabric that binds systems together.
This shift exposes weaknesses in legacy identity models that were designed for centralized directories, predictable endpoints, and slow change cycles. Static credentials persist longer than they should. Over-privileged roles accumulate silently. Visibility across machine identities remains fragmented. Authentication becomes a checkpoint rather than a continuous signal. Attackers exploit these gaps by blending into legitimate traffic, escalating privileges incrementally, and moving laterally across trusted identity relationships. Identity-native architecture directly confronts this reality by treating identity telemetry as a security sensor and identity policy as an enforcement engine rather than a simple access gate.
Beyond individual breaches, the economic and operational consequences amplify the urgency. Identity incidents disrupt supply chains, expose regulated data, compromise intellectual property, and erode trust at scale. Regulatory frameworks increasingly emphasize identity governance, auditability, and least-privilege enforcement. Insurance providers evaluate identity maturity as a risk indicator. Customers demand proof of digital trustworthiness. Identity is no longer an internal IT concern — it is a market signal and a reputational asset. Organizations that fail to modernize their identity posture risk structural fragility in a world where identity events drive operational continuity.
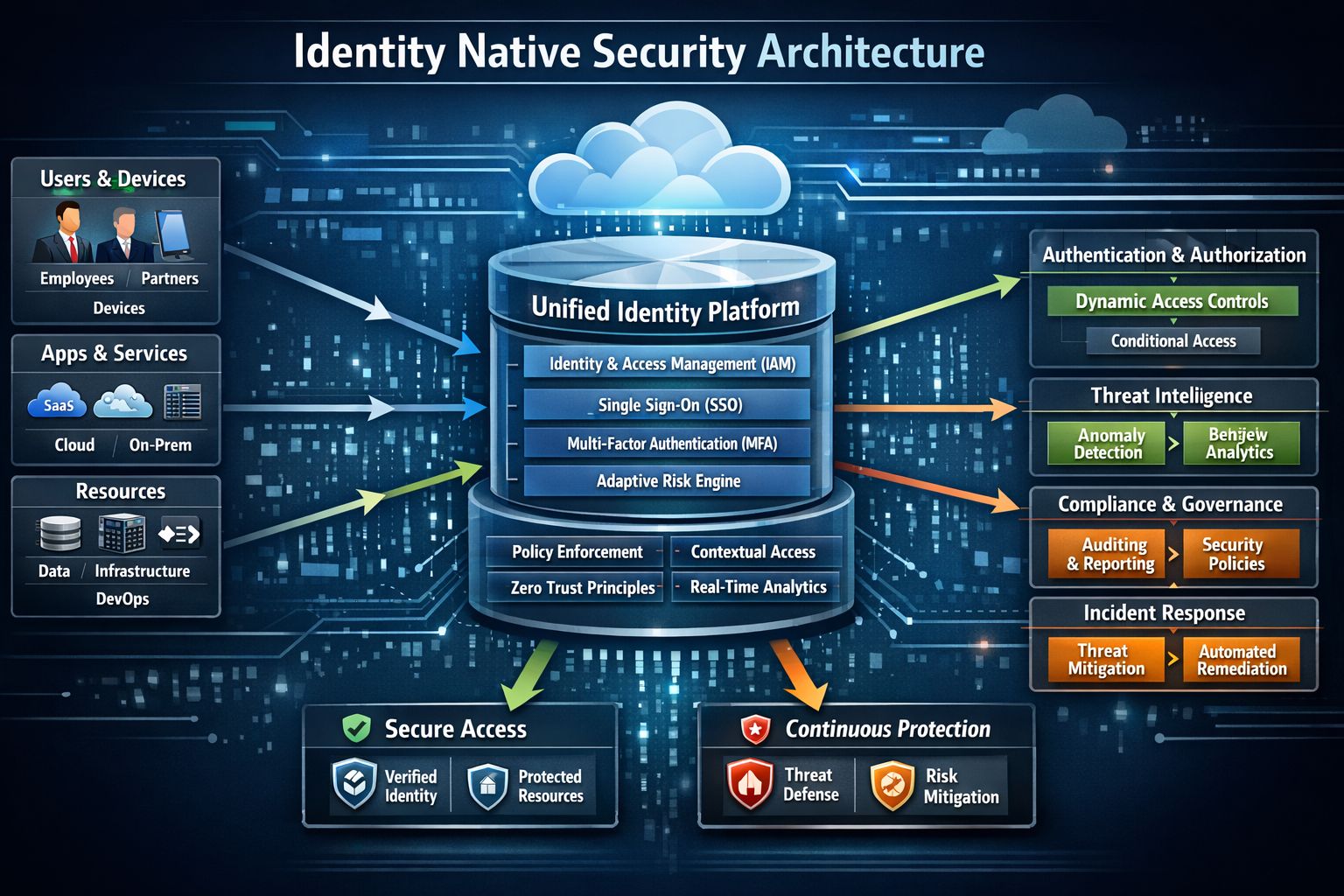
Core Pillars of Identity Native Security Architecture
Identity-native architecture is not a single product or vendor stack. It is a design discipline that integrates policy, telemetry, automation, governance, and cryptographic trust across every layer of digital operations. Its strength lies in consistency and composability. When implemented correctly, identity-native systems reduce complexity by making trust measurable, programmable, and enforceable across heterogeneous environments.
Below are the definitive pillars that operationalize identity-native security:
Foundational Pillars
Universal Identity Coverage
Every entity receives a governed identity: humans, workloads, APIs, containers, scripts, IoT devices, and autonomous agents. Each identity carries lifecycle management, ownership, cryptographic verification, and auditability.Zero Trust Enforcement
No implicit trust exists based on location, network segment, or prior authentication. Every request is evaluated continuously using dynamic risk signals and contextual intelligence.Continuous Authentication and Authorization
Access decisions adapt in real time based on device posture, behavioral patterns, threat intelligence feeds, workload integrity, and environmental risk scoring.Least Privilege Automation
Permissions are minimized automatically using just-in-time provisioning, ephemeral credentials, and policy-driven entitlement expiration.Policy as Code Governance
Identity rules are version-controlled, testable, auditable, and embedded directly into CI/CD pipelines and infrastructure automation workflows.Identity Telemetry and Analytics
Authentication flows, privilege elevation events, API calls, and behavioral anomalies feed security analytics platforms for detection and response automation.Cryptographic Trust Anchoring
Keys, certificates, hardware roots of trust, workload identity federation, and mutual authentication establish verifiable trust chains across systems.
Implementation Standards and Operational Maturity
Implementing identity-native architecture requires alignment with recognized security standards and operational frameworks. Organizations must avoid building isolated identity silos that replicate the fragmentation they are attempting to eliminate. Standards provide interoperability, audit alignment, vendor neutrality, and scalability across evolving platforms.
Key standards and frameworks that support identity-native maturity include:
NIST Zero Trust Architecture (SP 800-207) for policy enforcement and continuous verification
ISO/IEC 27001 and 27002 for governance, risk management, and control assurance
NIST Identity Guidelines (SP 800-63) for identity proofing and authentication assurance
OAuth 2.0, OpenID Connect, and SAML for federation and authorization interoperability
FIDO2 and WebAuthn for passwordless authentication
SPIFFE and SPIRE for workload identity federation
CIS Critical Security Controls for access governance and credential protection
SOC 2 and PCI DSS for compliance alignment
Operational maturity requires integrating these standards into automated workflows rather than manual audits. Identity governance platforms must synchronize with cloud infrastructure, HR systems, DevOps pipelines, and security monitoring tools. Policy enforcement should operate at machine speed. Access certifications should be continuous rather than quarterly. Incident response playbooks must integrate identity telemetry as a first-class signal rather than a supporting log source.
Equally important is cultural alignment. Security teams must collaborate with developers, platform engineers, compliance officers, and business stakeholders. Identity-native security becomes an engineering practice rather than a compliance obligation. Training programs must elevate identity fluency across disciplines. When identity policies become part of deployment pipelines and infrastructure templates, security shifts from reactive enforcement to proactive resilience.
Why Developers Are Embracing Identity Native Models
Modern developers operate in environments defined by speed, scale, and automation. Infrastructure is ephemeral. Services scale dynamically. APIs form complex dependency graphs. Hard-coded secrets and static credentials introduce operational risk and deployment friction. Identity-native models address these realities by replacing brittle credential management with federated trust and policy-driven access.
Developers benefit from identity-native systems in several practical ways. Service-to-service authentication becomes automatic through workload identity federation. Secrets management complexity decreases as ephemeral tokens replace static keys. Authorization policies can be expressed declaratively and tested in pipelines. Zero trust patterns enable secure internal APIs without reliance on network segmentation. Observability improves as identity telemetry exposes service interactions clearly. Secure defaults reduce cognitive overhead, allowing developers to focus on product innovation rather than security plumbing.
The cultural shift is equally important. Identity-native design aligns with DevSecOps principles by embedding security controls directly into build systems and runtime environments. Developers gain confidence that access controls evolve dynamically as systems change. Rollbacks and infrastructure rebuilds inherit security posture automatically. Incident response accelerates because identity telemetry provides immediate clarity on what accessed what, when, and why. When developers experience security as an accelerator rather than a barrier, adoption becomes organic rather than mandated.

Why Educators Should Teach Identity First Security
Cybersecurity education has historically emphasized perimeter defense, malware analysis, and network monitoring. While these skills remain valuable, they no longer represent the dominant risk vectors facing modern enterprises. Graduates entering the workforce encounter identity-driven cloud environments, automation pipelines, API ecosystems, and distributed architectures that require a fundamentally different mental model of trust.
Teaching identity-first security prepares students to design systems where access governance, authentication assurance, policy automation, and behavioral analytics are foundational rather than supplemental. Students learn to reason about trust boundaries abstractly rather than geographically. They understand how permissions propagate across systems. They learn how identity telemetry informs detection engineering. They become fluent in standards-based federation, cryptographic identity, and policy-driven enforcement. This skillset aligns directly with enterprise demand across cloud engineering, security architecture, compliance, and platform reliability roles.
Educational institutions also play a broader societal role in shaping digital resilience. As governments, healthcare systems, educational platforms, and critical infrastructure increasingly depend on identity-driven access control, the workforce must possess deep competence in identity governance and secure design. Integrating identity-native principles into curricula ensures that future professionals can build systems that scale securely without inheriting fragile legacy assumptions.
Business Impact Beyond Security
The value of identity-native architecture extends well beyond risk reduction. When trust becomes programmable and measurable, organizations gain operational clarity, regulatory confidence, and strategic agility. Access audits become faster and more accurate. Compliance reporting becomes automated. Mergers and acquisitions integrate more smoothly as identity federation simplifies system alignment. Vendor ecosystems become safer through standardized access controls. Customer trust strengthens when digital interactions demonstrate consistent security posture.
Operational efficiency improves as automation replaces manual provisioning workflows. Helpdesk tickets decrease as passwordless authentication reduces friction. Incident response accelerates because identity telemetry pinpoints anomalous behavior quickly. Cloud adoption accelerates because identity controls scale across environments consistently. Business units gain confidence to innovate because security becomes embedded rather than reactive. These effects compound over time, producing measurable gains in resilience, productivity, and reputation.
Financially, organizations benefit from reduced breach exposure, lower operational overhead, improved audit outcomes, and optimized insurance risk profiles. Strategically, identity-native maturity positions enterprises to adopt emerging technologies — AI agents, autonomous systems, decentralized platforms — without compromising trust. Identity becomes a strategic asset rather than a technical constraint.
The Future Identity as Digital Infrastructure
As digital ecosystems continue to evolve, identity will increasingly function as foundational infrastructure — much like electricity or networking. Autonomous agents will transact independently. Machine-to-machine interactions will outnumber human sessions dramatically. Regulatory environments will demand cryptographic accountability. Supply chains will require verifiable provenance. Trust will need to operate at machine speed with minimal human intervention.
Identity-native architecture enables this future by providing a scalable trust fabric capable of supporting billions of identities across heterogeneous platforms. Policy engines will increasingly integrate artificial intelligence to adapt dynamically to emerging threats. Cryptographic identity frameworks will extend into hardware roots of trust and decentralized verification models. Telemetry-driven intelligence will power predictive defense rather than reactive remediation. Governance automation will compress compliance cycles from months to minutes.
The organizations that succeed will be those that treat identity as engineered infrastructure rather than administrative overhead. They will invest in standards alignment, automation maturity, cross-functional fluency, and continuous improvement. They will recognize that trust is not a static property — it is an operational capability that must evolve continuously as technology reshapes how systems interact.

Final Thoughts on Engineering Trust at Scale
Identity-native security architecture represents a turning point in how organizations conceptualize protection, accountability, and resilience. It replaces fragile assumptions with measurable controls. It transforms trust from implicit belief into operational certainty. It aligns engineering velocity with security confidence. It allows organizations to scale complexity without surrendering control.
The journey requires intentional design, cultural alignment, and disciplined execution. It demands investment in standards, automation, telemetry, and education. It challenges legacy mental models that equate security with perimeter defense rather than behavioral assurance. Yet the rewards extend far beyond reduced risk. Identity-native maturity unlocks innovation, strengthens digital credibility, and creates operational clarity in environments that would otherwise become unmanageable.
For security professionals, developers, educators, and business leaders alike, identity-native architecture offers a path toward building systems that remain trustworthy even as technology accelerates relentlessly forward. Trust becomes something engineered deliberately — embedded into every transaction, every workload, and every interaction — quietly shaping a safer digital world at scale.

Subscribe to CyberLens
Cybersecurity isn’t just about firewalls and patches anymore — it’s about understanding the invisible attack surfaces hiding inside the tools we trust.
CyberLens brings you deep-dive analysis on cutting-edge cyber threats like model inversion, AI poisoning, and post-quantum vulnerabilities — written for professionals who can’t afford to be a step behind.
📩 Subscribe to The CyberLens Newsletter today and Stay Ahead of the Attacks you can’t yet see.





